How To Choose the Right Type of Glass for Your Windows
When it comes to home improvement, one crucial aspect often overlooked is the type of glass used in your windows. The window glass you choose impacts everything from energy efficiency to safety, aesthetics, and durability. With so many types of glass for windows available on the market, knowing the right kind for your home can be overwhelming. This article dives deep into the world of window glass types, helping you choose the right glass that fits your needs, budget, and style. Whether you're replacing old windows or installing new ones, understanding the different types of window glass is essential to making an informed decision.
1. What Are the Common Types of Window Glass?
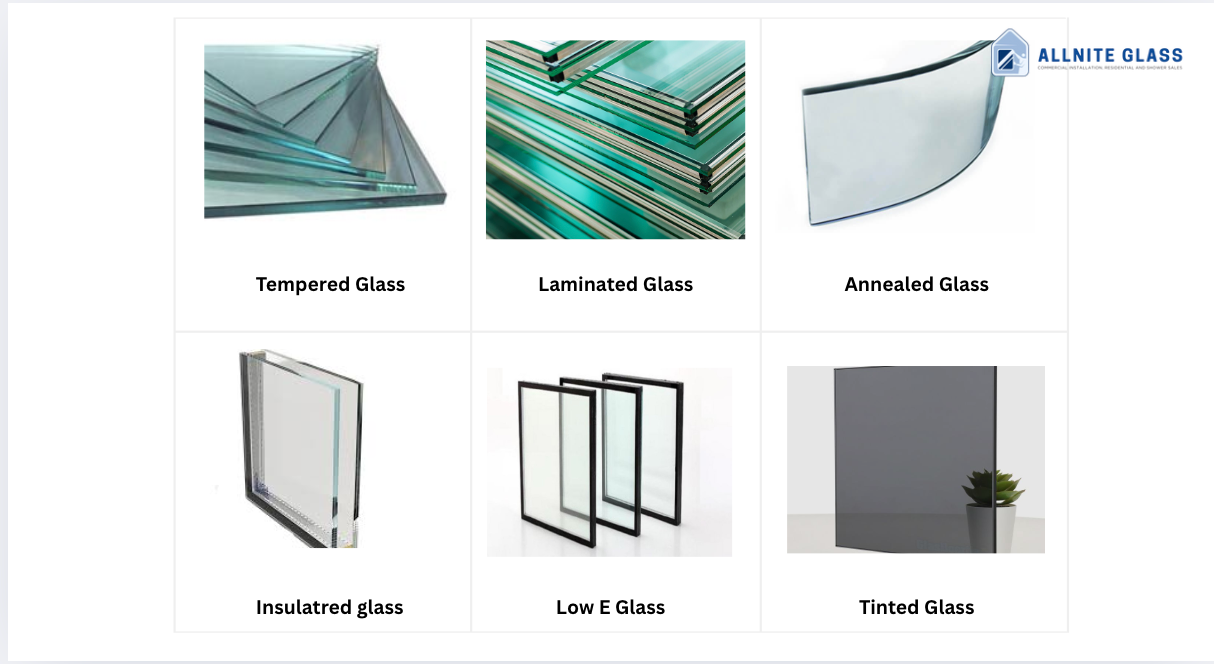
The most frequently used glass for windows includes annealed glass, tempered glass, and laminated glass. Annealed glass is the standard glass type, also called standard glass, which is slowly cooled after being heated, making it more stable but less resistant to impact.
In contrast, tempered glass is heated and rapidly cooled, making it about four to five times stronger than annealed glass. It’s commonly referred to as safety glass because it shatters into small, less dangerous pieces when broken. Laminated glass consists of two or more panes of glass bonded with a plastic interlayer, holding the shards together if the glass breaks, providing enhanced security and sound insulation.
Each glass type offers distinct advantages, making it important to understand which fits your specific window needs.

2. What Is Tempered Glass and Why Is It Important?
Tempered glass is a type of window glass that undergoes controlled heating and rapid cooling, which strengthens the material significantly. This process makes it much more durable and resistant to heat, impacts, and thermal stress compared to annealed glass. Because of its strength, tempered glass is often used in areas prone to accidental impacts or severe weather.
One key feature of tempered glass is safety. When it breaks, it shatters into tiny granular chunks instead of sharp shards, reducing the risk of injury. This property is why tempered glass is also known as safety glass. For homes with children or pets, or for windows exposed to external hazards, tempered glass offers peace of mind.
3. How Does Laminated Glass Differ from Other Glass Types?
Laminated glass is made by sandwiching a thin plastic layer between two or more panes of glass. This design keeps the glass intact even when broken, preventing dangerous shards from flying and improving security against break-ins. The plastic interlayer also provides excellent noise reduction, making laminated glass popular in urban settings.
Unlike tempered glass, which breaks into small pieces, laminated glass stays mostly in one piece due to the bonding layer. This characteristic makes laminated glass ideal for windows and doors where both safety and sound insulation are priorities. Additionally, laminated glass is made with UV-filtering capabilities, which protect interior furnishings from fading caused by sunlight.
4. What Is Annealed Glass and When Should It Be Used?
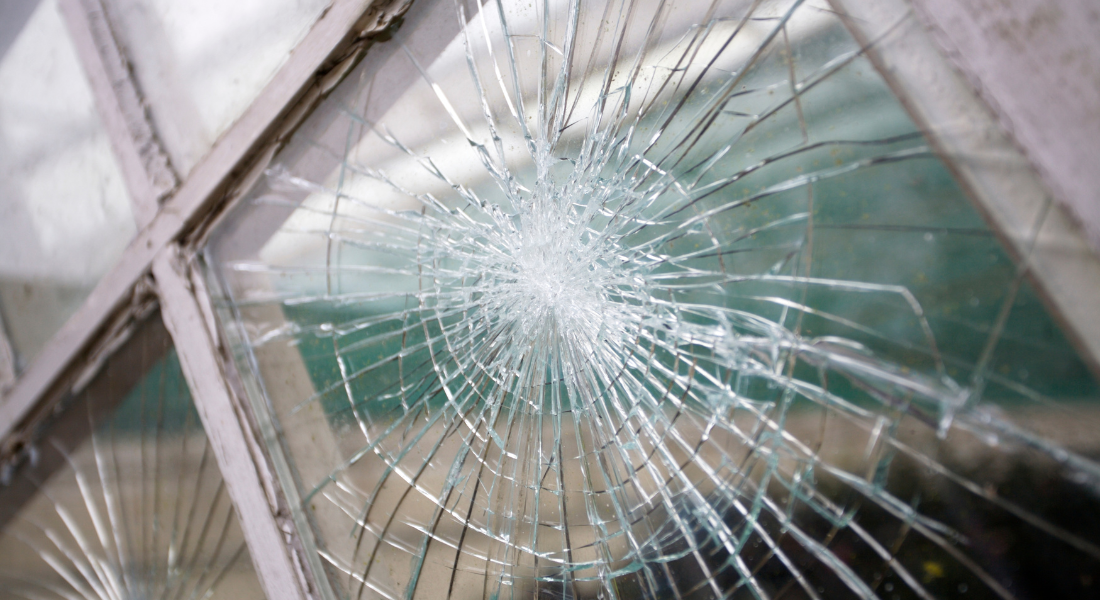
Annealed glass is the traditional type of window glass created by slowly cooling molten glass to relieve internal stresses. While it’s the most economical and commonly used, annealed glass is not as strong or safe as tempered or laminated glass. When annealed glass breaks, it forms large, sharp shards, which can be hazardous.
Because of its properties, annealed glass is best suited for windows in low-risk areas or where strength and safety glass are not critical concerns. It can also be used in decorative glass panels or situations where custom shaping and cutting are needed, as annealed glass is easier to work with before installation.
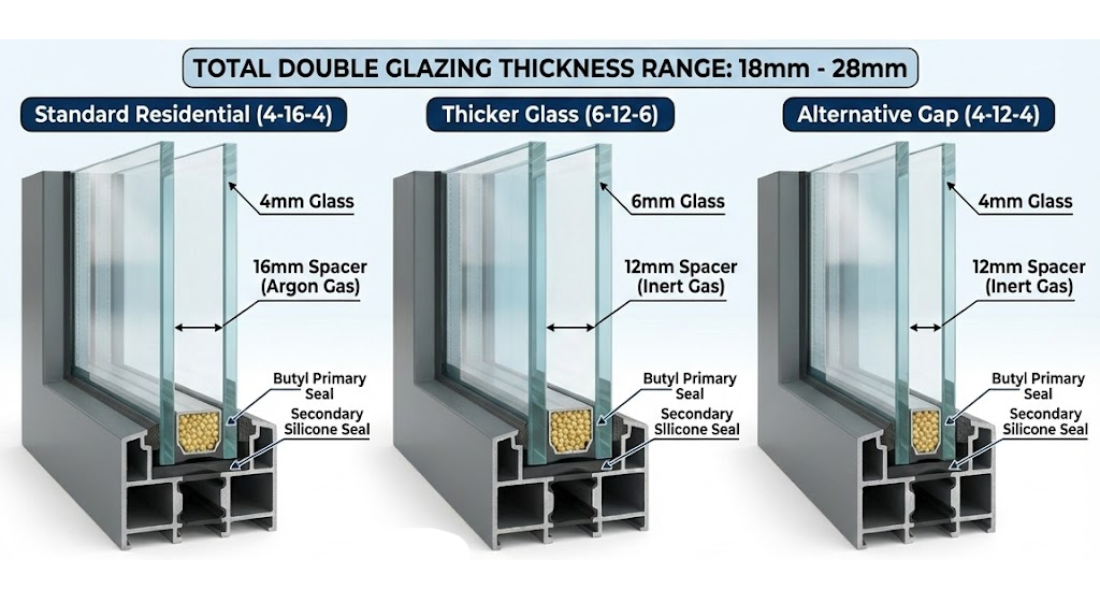
5. What Are Insulated Glass Units and How Do They Improve Energy Efficiency?
Insulated glass units (IGUs) are made by sealing two or more panes of glass together with a gap filled by air or inert gas such as argon. This gap acts as a thermal barrier, significantly reducing heat transfer between the interior and exterior of your home. This improvement leads to better energy efficiency and helps maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
The type of insulated glass can vary, including double-pane windows and triple-pane windows, each offering higher energy savings than single-pane options. The gas between the panes reduces convection and conduction, making insulated glass units a popular choice for energy-efficient window glass in modern homes.
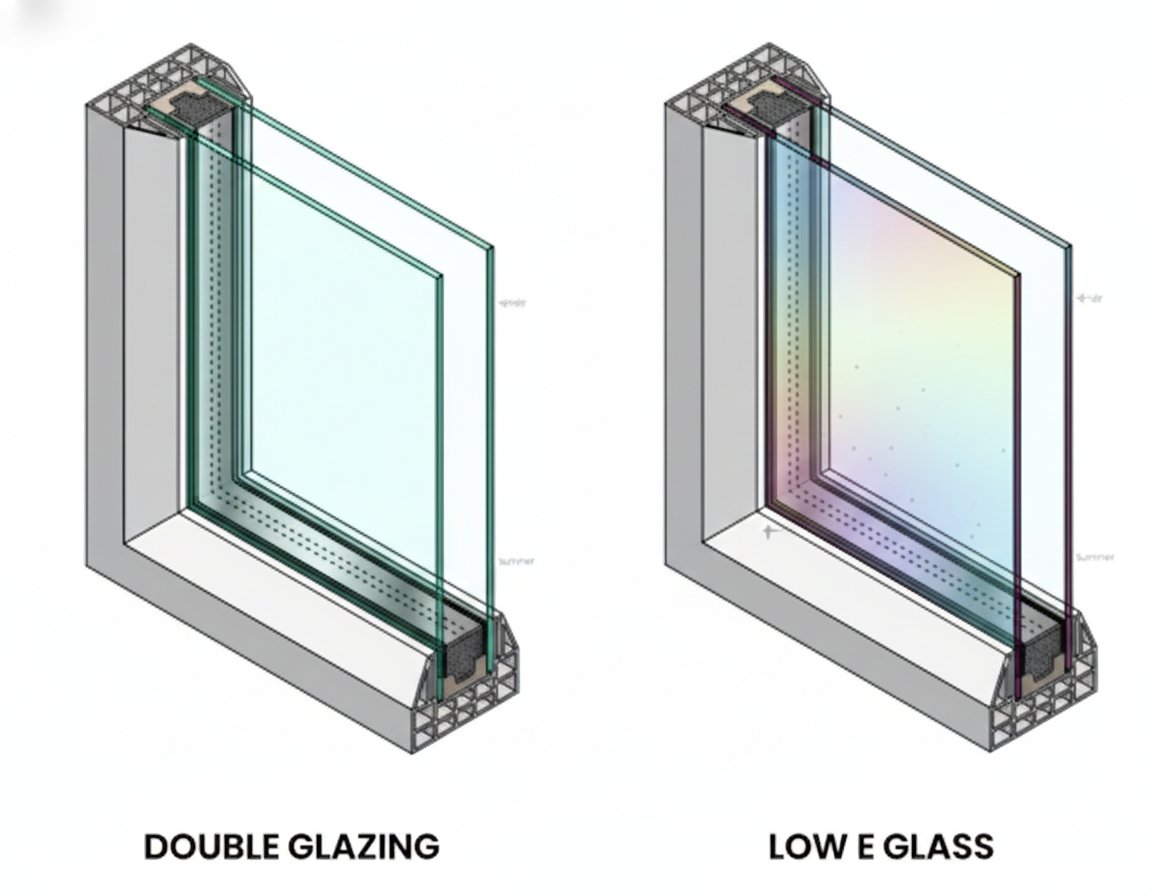
6. What Is Low-E Glass and How Does It Save Energy?
Low-e glass, short for low-emissivity glass, has a microscopically thin coating that reflects infrared heat while allowing visible light to pass through. This feature helps keep your home warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer by reducing heat loss and gain through the windows.
Using low-e glass can significantly boost your home’s energy efficiency, lowering heating and cooling costs. Different types of low-e coatings are available, each designed for specific climates and sun exposures. When combined with insulated glass units, low-e glass offers one of the best solutions for reducing energy bills and enhancing indoor comfort.
7. When Should You Consider Impact-Resistant Glass for Your Windows?
Impact-resistant glass is engineered to withstand severe weather conditions like hurricanes or forced entry attempts. This type of glass often combines laminated glass layers with strong interlayers and is tested to meet stringent safety and security standards.
For homes in hurricane-prone areas or locations with high burglary rates, investing in impact-resistant glass for your windows and doors is a smart choice. It not only provides protection but also meets insurance requirements in some regions, potentially lowering premiums.
8. How Does Tinted Glass Affect Window Performance and Privacy?
Tinted glass contains additives or coatings that reduce the amount of sunlight and UV radiation passing through the window. This helps reduce glare, protects furniture from fading, and lowers heat buildup inside the home.
Besides energy efficiency benefits, tinted glass also adds privacy by limiting visibility from the outside without sacrificing natural light. This makes it a great option for windows facing busy streets or neighbors. Various shades and colors are available, allowing homeowners to choose the right balance between aesthetics and function.
9. What Is Heat-Strengthened Glass and How Is It Different from Tempered Glass?
Heat-strengthened glass is heated and cooled more slowly than tempered glass, resulting in glass that is stronger than annealed glass but not as strong as tempered glass. It offers better resistance to thermal stress and is less prone to breakage from temperature fluctuations.
While heat-strengthened glass does not shatter into small granules like tempered glass, it is still safer and stronger than regular glass. It’s often used in architectural applications where moderate strength and thermal resistance are needed without the full safety glass requirements of tempered glass.
10. How to Choose the Right Type of Glass for Your Home Windows?
Choosing the right type of glass depends on your specific needs, including safety, energy efficiency, budget, and aesthetic preferences. For homes needing window glass replacement, it’s crucial to consider factors such as:
- The level of impact resistance required
- The climate and the need for energy-efficient window glass
- Whether noise reduction or UV protection is important
- Budget constraints and maintenance considerations
Combining insulated glass units with low-e coatings is an excellent approach for most modern homes seeking to save on energy bills. For safety, tempered or laminated glass is recommended. Consulting with a window professional to evaluate your home’s requirements can help you make the best choice.
Trust Professionals When Choosing the Right Window Glass
We’re Allnite Glass — and we’re here to help! With years of experience in both commercial and residential glass repair, our team knows how to match the ideal glass type to your specific needs! . Whether you’re focused on energy efficiency, safety, noise reduction, or long-term durability. From tempered glass and laminated glass to advanced low-e coatings and insulated glass units, we’ll guide you through the many types of glass for windows and ensure flawless installation every time. Trust Allnite Glass to deliver the right solution with unmatched craftsmanship, professionalism, and care.
Summary: Key Points to Remember
- Window glass types include annealed, tempered, laminated, insulated, low-e, tinted, and impact-resistant glass.
- Tempered glass is stronger and safer than standard annealed glass, which breaks into small pieces.
- Laminated glass holds together when broken, enhancing security and noise reduction.
- Insulated glass units improve energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer.
- Low-e glass coatings reflect heat, saving energy and increasing comfort.
- Impact-resistant glass is ideal for high-risk areas prone to storms or break-ins.
- Tinted glass reduces glare, UV damage, and improves privacy.
- Heat-strengthened glass offers moderate strength and thermal resistance, sitting between annealed and tempered glass.
- Selecting the right type of glass depends on safety, energy goals, aesthetics, and budget.
- Consult professionals and consider combining different glass types to maximize performance.
By understanding these types of glass for windows, you can confidently select the right glass for your windows and enjoy a safer, more comfortable, and energy-efficient home.
FAQs
Q. What Is the Most Durable Type of Window?
A. The most durable type of window typically combines a strong frame material like fiberglass or vinyl with impact-resistant glass. Among glass options, laminated glass and tempered glass are considered the most durable. Tempered glass is heat-treated to be several times stronger than regular glass and resists breaking under stress. Laminated glass, made by bonding two layers of glass with a plastic interlayer, holds together even when broken and provides added strength, making it ideal for extreme weather or high-security areas.
Q. What Is the Most Efficient Window Glass?
A. The most energy-efficient window glass is typically a low-e (low-emissivity) insulated glass unit. These windows feature two panes of glass separated by a gas-filled space (usually argon or krypton) and coated with a thin low-e layer that reflects heat. This combination reduces heat loss in winter and blocks solar heat gain in summer, offering optimal energy efficiency. In colder climates, triple-pane windows provide even better insulation.
Q. Which Type of Window Lasts the Longest?
A. Fiberglass windows combined with insulated low-e glass tend to last the longest. The glass itself, when properly installed and maintained, can last decades, especially when using laminated or tempered glass, which resists breakage and weather damage. Frame material, weather conditions, and maintenance play significant roles in determining the overall lifespan of the window system.
Q. How Long Can Glass Windows Last?
A. With proper care, glass windows can last anywhere from 20 to 50 years or more. Insulated glass units (especially double or triple-pane) may develop seal failures after 15–30 years, depending on quality and installation. However, laminated and tempered glass windows are built to last and can withstand wear, impacts, and temperature changes over time. Regular inspections and timely window replacement when necessary will help maximize the lifespan of your windows and glass.