Double Glazing Thickness Explained: How Thick Is Double Glazed Glass and Why It Matters
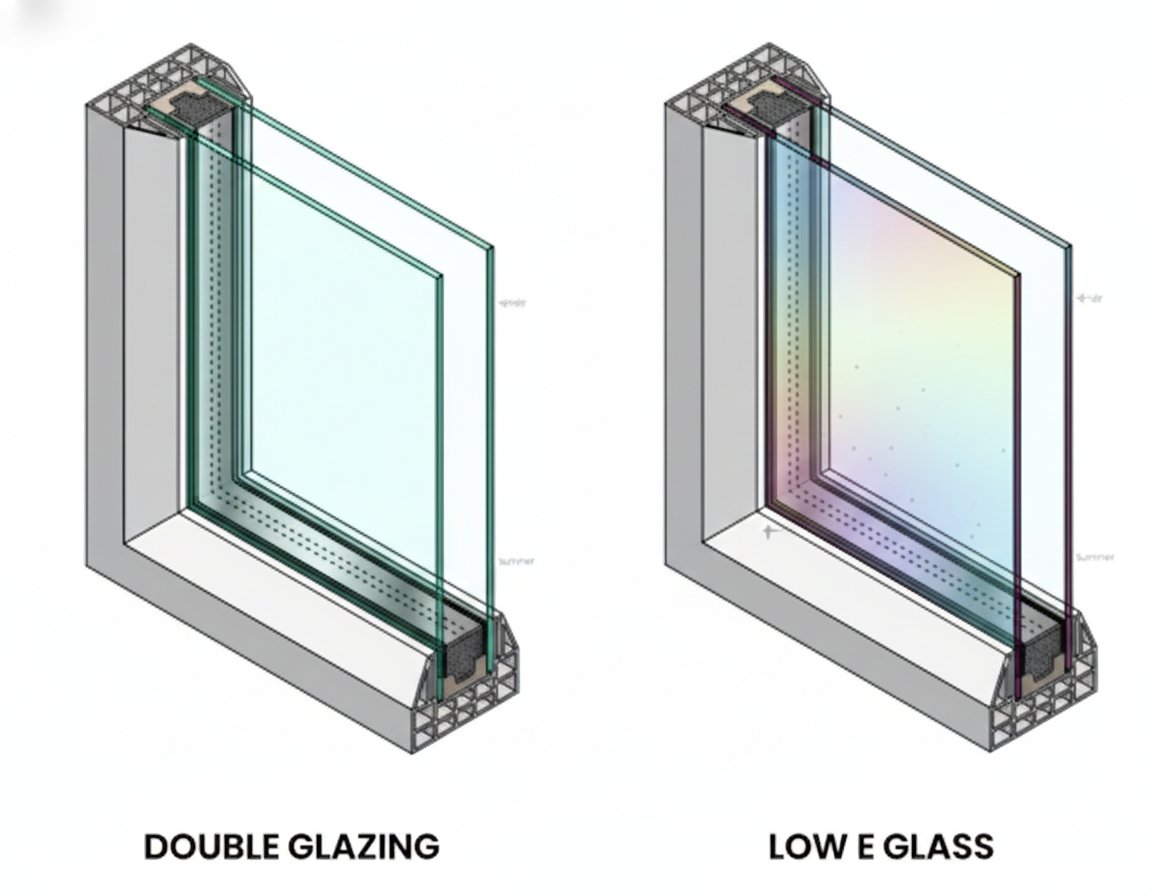
Glazing thickness has a direct impact on how well double-glazed windows perform. From insulation and energy efficiency to condensation control and noise reduction, the thickness of glass plays a major role in comfort and long-term savings.
This guide breaks down double glazing thickness in simple terms. You’ll learn how thick double-glazed glass typically is, how panes and spacers work together, and how choosing the right glass thickness can lower energy bills and improve overall window performance.
What Is Glazing and Why Does Thickness Matter?
Glazing refers to the glass installed within a window frame, and its thickness determines how effectively it can insulate a home. When glazing thickness increases, the window is better able to slow heat transfer between the inside and outside, which improves insulation and comfort.
Thickness also affects durability and soundproofing. A thicker pane of glass can reduce outside noise and provide better resistance against weather exposure. Choosing the right glazing thickness helps balance insulation, cost, and performance for different types of window installations.
How Thick Is Double Glazed Glass?
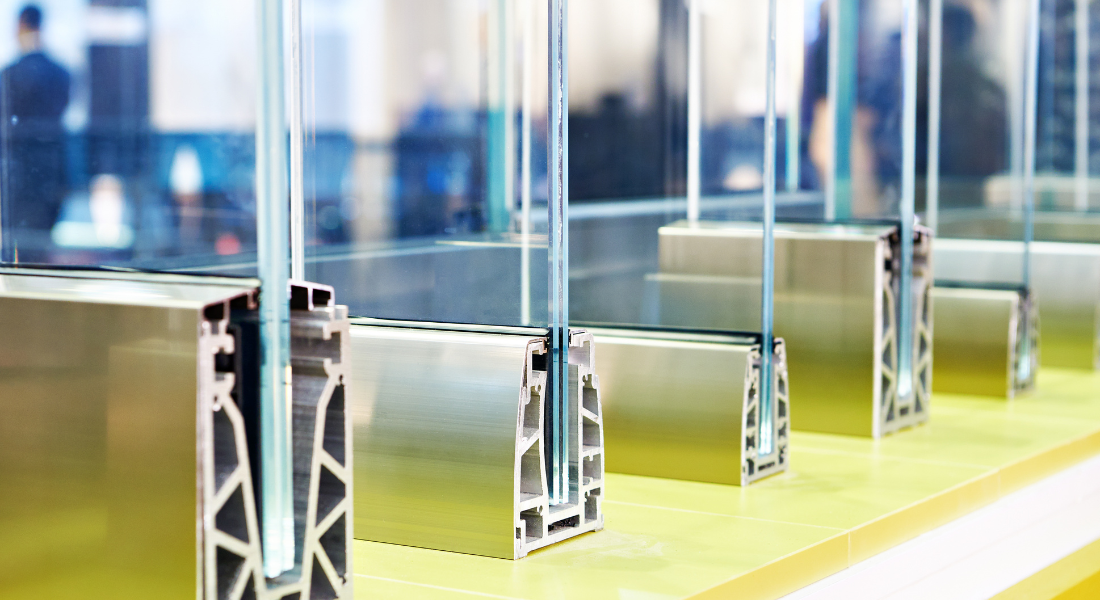
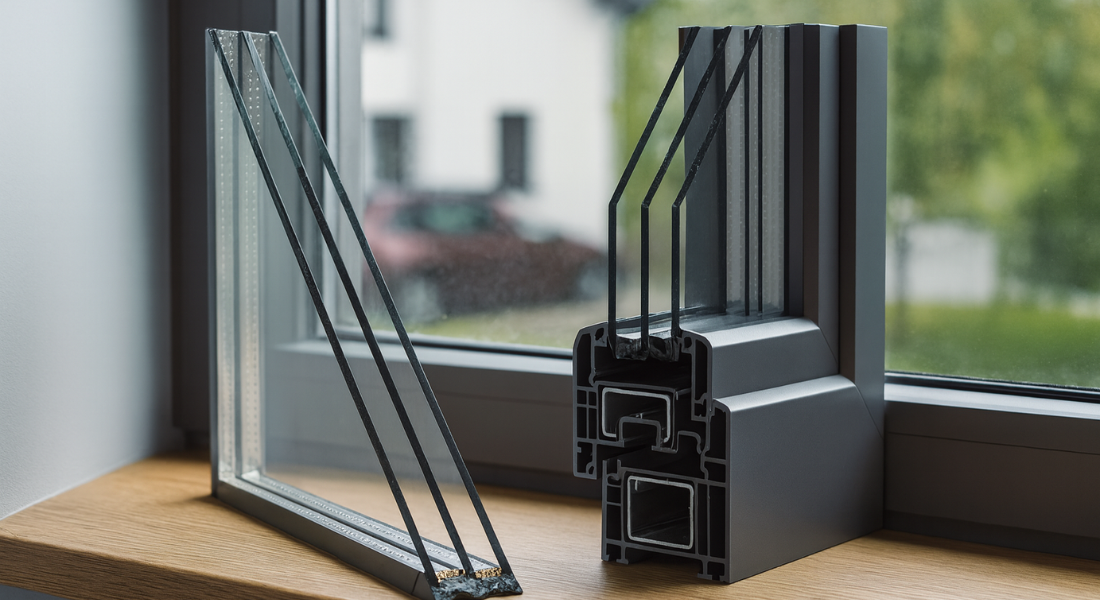
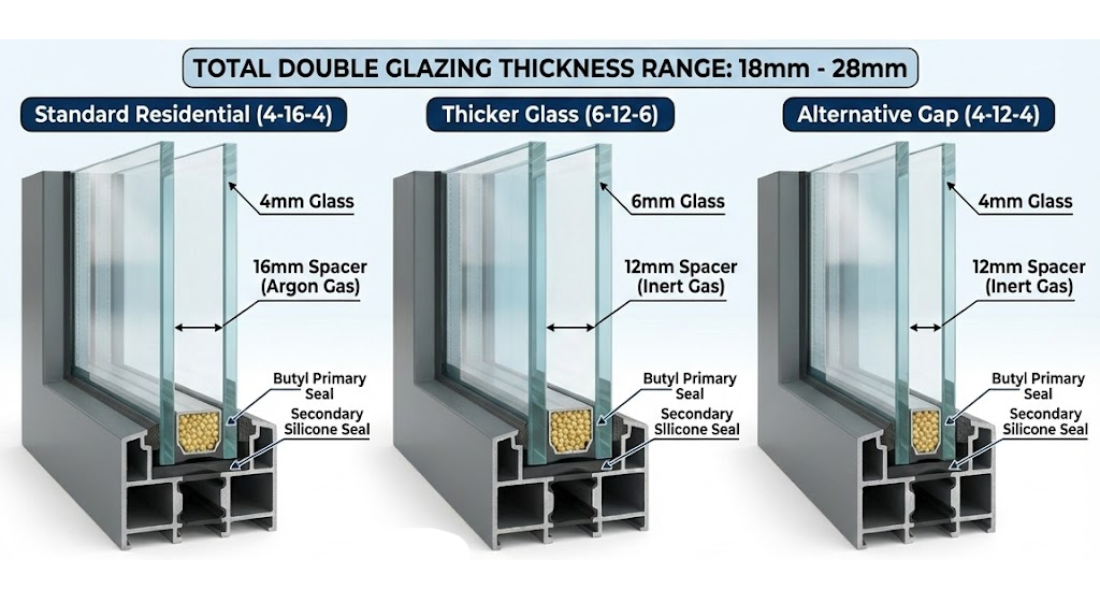
Double-glazed windows consist of two panes of glass separated by a spacer. Each glass pane typically measures between 4mm and 6mm thick, while the gap between the panes adds additional overall thickness.
When combined, the total thickness of double glazing usually falls between 18mm and 28mm. This thickness of double glazing allows air or inert gas to sit between the panes, helping to insulate the window and reduce heat loss.
What Is the Standard Glass Thickness Used in Double Glazing?
Standard glass thickness for most residential double-glazed windows uses two panes of glass that are commonly 4mm thick. These panes are separated by spacer bars that create a gap, often between 12mm and 16mm.
This combination creates an insulated glass unit that offers solid thermal efficiency without adding excessive weight to the window frame. Standard glass thickness is widely used because it balances insulation, window costs, and compatibility with existing window frames.
How Do Panes and Spacers Affect Glazing Thickness?
A double glazing unit consists of two panes of glass separated by a spacer. The spacer determines the gap between the glass panes and plays a key role in insulation and condensation control. The glass is separated by a gap that is often filled with argon or another inert gas.
Spacers also affect the overall thickness of the glazing units. Wider spacers improve insulation up to a point, but too wide a gap can reduce thermal efficiency by allowing heat transfer through air movement.
Does Thicker Glass Improve Energy Efficiency?
Thicker glass alone does not always mean better energy efficiency. While thicker glass can add strength and noise reduction, insulation primarily comes from the space between panes and the gas used inside the glazing units.
Energy efficiency improves when thicker glass is paired with proper insulation, low-e coatings, and argon-filled gaps. Together, these features reduce heat loss and help lower heating and cooling costs throughout the year.
How Does Double Glazing Thickness Reduce Heat Transfer?
Double glazing works by slowing heat transfer through multiple layers. Each pane of glass and the gap between them act as barriers that reduce heat loss during cold months and limit heat entering the home during warmer periods.
The thickness of glass and the spacer distance both influence how well the glazing can insulate. Properly designed double-glazing units reduce heat transfer more effectively than a single-pane window, helping maintain indoor temperatures.
Can Glazing Thickness Help with Condensation and Noise Reduction?
Glazing thickness can help reduce condensation by keeping the inner pane warmer, which limits moisture buildup. When condensation is reduced, windows remain clearer and less prone to mold or moisture damage.
Thicker glass also improves noise reduction, especially in homes located near busy roads or noisy areas. Using thicker glass panes or laminated glass can significantly reduce sound transmission through windows.
How Does Double Glazing Compare to Triple Glazing?
Double glazing uses two panes of glass, while triple glazing adds a third pane of glass and an extra insulating gap. Triple glazing provides additional insulation and thermal efficiency, especially in colder climates.
However, triple glazing increases overall thickness, window costs, and weight. For many homes, double-glazed windows offer a better balance between insulation, affordability, and performance.
What Thickness Should You Choose for a Replacement Window?
The right glass thickness depends on the type of window, climate, and budget. For most replacement window projects, standard double-glazing thickness provides sufficient insulation and energy efficiency.
Homes in noisy areas or extreme climates may benefit from thicker glass or laminated glass. An experienced installer can help determine the ideal thickness based on existing window frames and performance goals.
How Does Glass Thickness Affect Window Costs and Installation?
As glazing thickness increases, window costs typically rise due to heavier materials and more complex installation. Thicker glazing units may require reinforced window frames or specialized installation methods.
Despite higher upfront costs, choosing the right thickness can result in long-term energy savings. Improved insulation lowers heating and cooling costs, making double-glazed windows a worthwhile investment over time.
Read Our Other Blog!
If you’re exploring glazing thickness because you’re dealing with older or aging windows, it’s also worth understanding how repairs compare to full replacement—especially in historic or older homes. Our blog
“Repairing a Broken Window Pane in an Old House: DIY Window Repair vs Replacement” walks through the unique challenges of older window systems, explains when a simple pane repair is possible, and highlights situations where replacement is the safer and more cost-effective option.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. How thick is double glazing in total?
A. Double glazing thickness usually ranges from 18mm to 28mm, depending on pane thickness and spacer size.
Q. Is thicker glass always better for insulation?
A. Not always. Insulation depends on the combination of glass thickness, spacer width, and gas filling, not just thicker glass alone.
Q. What is the most common glass thickness used in double-glazed windows?
A. Most double-glazed windows use two 4 mm-thick glass panes with a spacer between them.
Q. Does glazing thickness affect condensation?
A. Yes. Proper glazing thickness helps keep the inner pane warmer, reducing condensation buildup.
Q. Is double glazing better than a single-pane window?
A. Yes. Double glazing provides better insulation, reduced heat transfer, and improved energy efficiency compared to a single pane.
Key Takeaways
- Glazing thickness affects insulation, energy efficiency, and comfort
- Double-glazed windows typically range from 18mm to 28mm thick
- Glass thickness works together with spacers and gas filling to insulate
- Thicker glass can reduce noise and condensation when designed properly
- Choosing the right thickness can lower energy bills and improve long-term performance