What Is The Difference Between Glass And Glazing
This article is worth reading because it breaks down glazing in plain language. You will learn what glaze means, how glazing and glass work together, and how the right window glass can improve energy efficiency and comfort. By the end, you will understand the options available and how to choose the right solution for your climate and building.
Window glaze plays a bigger role in homes and buildings than many people realize. From improving comfort and reducing heat loss to controlling UV exposure and lowering energy costs, window glazing is central to how modern glass and window glazing systems perform. Whether you are researching new windows, upgrading older ones, or simply trying to understand how glass and window systems work, this guide will give you a clear and practical explanation.
What Does Glaze Mean in Modern Construction?
The word glazing is often used in construction, but many people are unsure what it actually means. Glaze refers to the glass installed within a window opening and the method used to secure it. Historically, glazing involves making a pane of glass into timber using putty, but modern systems are far more advanced.
Today, glazing refers to a complete system. Glazing involves the glass itself, seals, spacers, and any coating added to the glass. The term glazing is also used to describe how the glass performs, not just how it is held in place. In other words, glaze refers to both function and structure.
Understanding glaze helps explain why some windows feel warmer, quieter, and more comfortable than others, even when they look similar from the outside.
How Does Window Glazing Work in Glass Windows?
Window glazing works by managing how heat, air, and light move through glass windows. A well-designed glaze reduces heat transfer through conduction and convection while still allowing visible light to enter the space.
A modern glaze may include multiple layers of glass, gas-filled cavities, and a low-e coating that reflects infrared heat. This setup helps insulate the building and maintain stable indoor temperatures. In winter, glazing helps reduce heat loss. In summer, it can limit solar heat gain.
Because glazing controls energy flow, it directly affects comfort, insulation, and overall energy efficiency.
What Are Glazed Windows and Why Do They Matter?
Glazed windows are windows that use one or more pane layers of glass secured into a frame using a glazing system. Nearly all residential and commercial buildings today rely on glazed windows for light, visibility, and protection from the elements.
The quality of the glaze determines how well the window performs. A poorly designed glaze may allow drafts, excess condensation, and temperature swings. A high-quality glaze improves insulation and reduces moisture issues.
Glazed windows matter because they influence comfort, durability, and long-term energy costs.
Glass and Window Glazing: How Glass and Window Systems Fit Together
Glass and window glazing describes how the glass and window components work as a single unit. The glass and window must function together to achieve good performance. Even the best glass will underperform if the glazing system or frame is poorly designed.
In a complete glazing system, the pane is sealed into the window frame using gaskets, spacers, and glazing points. This prevents air leaks and moisture intrusion around the perimeter. Good sealing is essential to control condensation and heat loss.
This integrated approach is why glazing specialists look at the entire window assembly, not just the glass itself.
Glass and Window Design: How the Frame and Pane Work as One
Each pane in a window has a role to play. The pane provides transparency and light, while the frame supports the structure and holds the glaze securely. The window frame also affects insulation and durability.
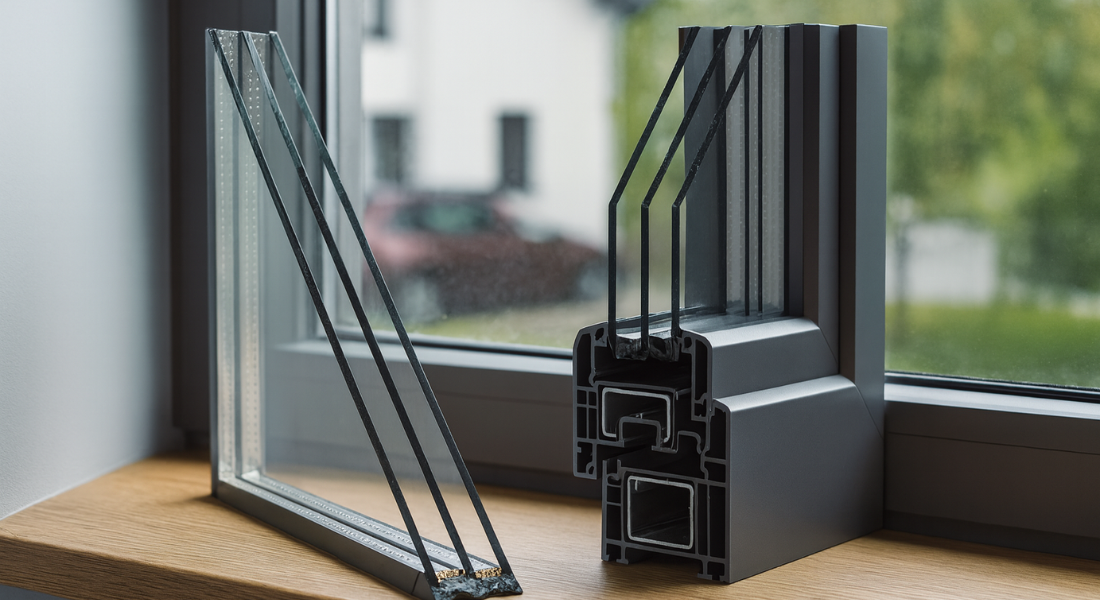
In multi-pane designs, two glass panes or even two glass panes combined with a third layer create an insulating system. The gap between the panes is carefully engineered to reduce conductive and convective heat transfer.
When glass within the frame is properly sealed and aligned, the entire system performs better, lasting longer and providing greater comfort.
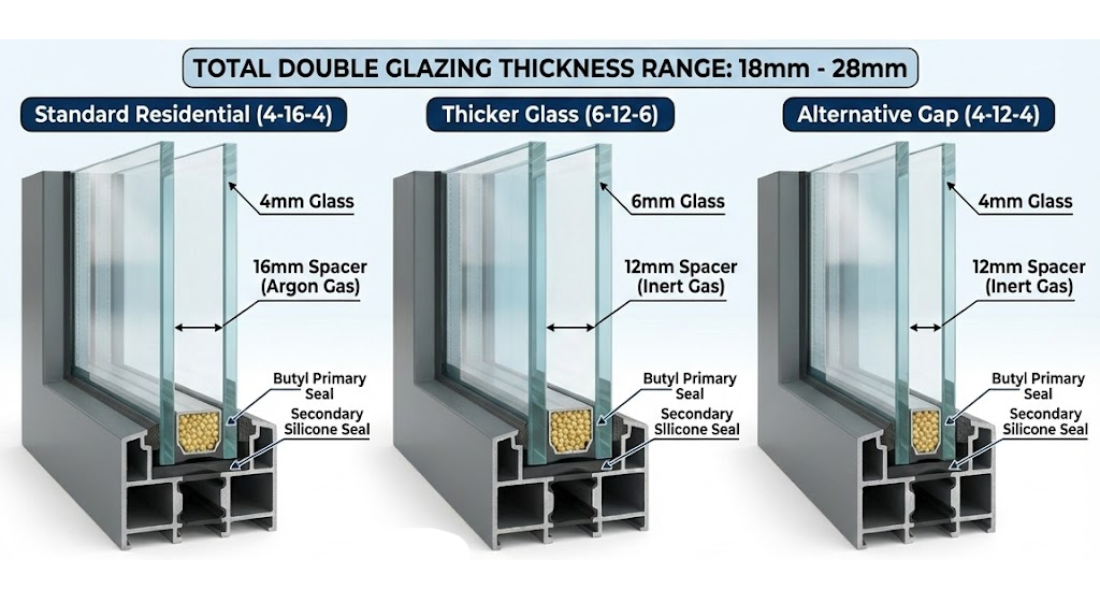
Double Glazing Explained: Why Two Panes Are Better Than One
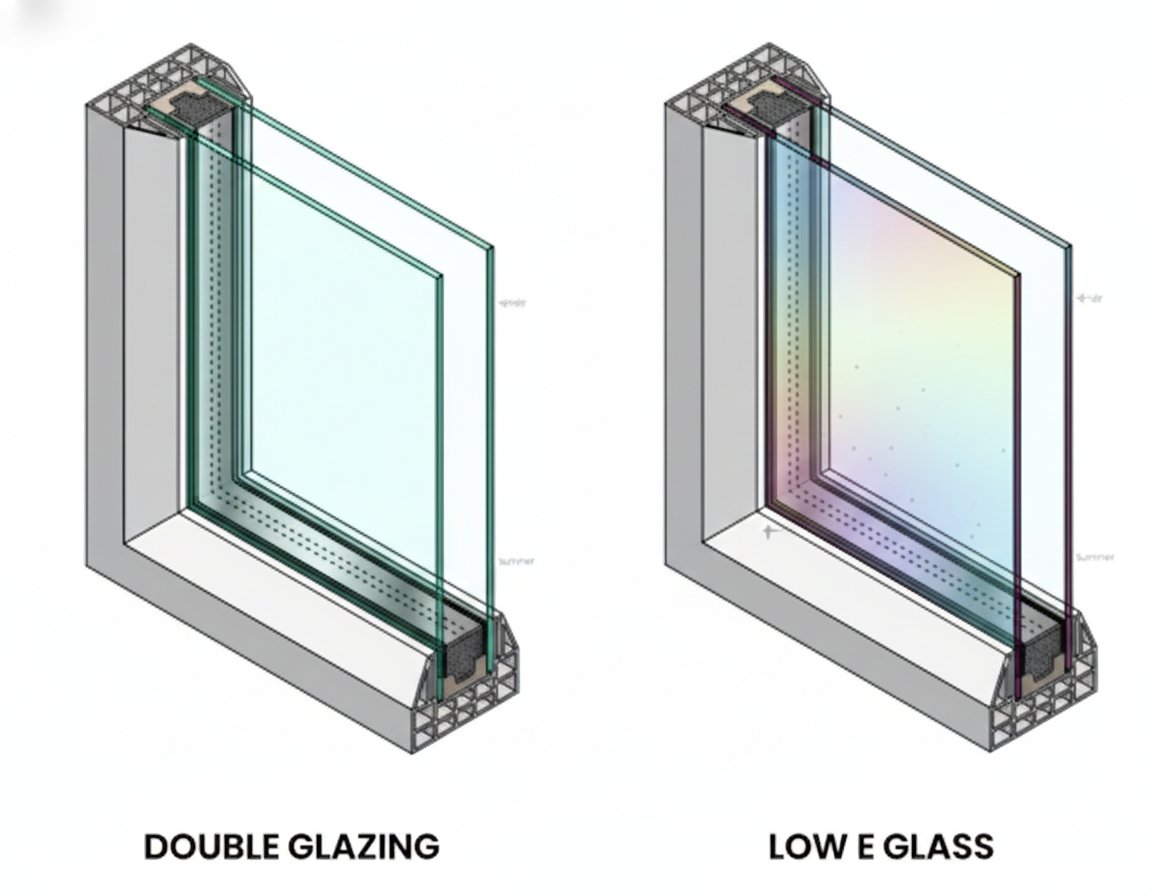
Double glazing is one of the most common and effective glazing solutions. It uses two panes of glass separated by a sealed cavity. This cavity is often filled with argon or krypton, both of which act as insulating gases.
A double glazing system reduces heat loss, improves insulation, and limits condensation. Compared to single glazing, it offers a major improvement in energy efficiency. Double glazing also helps reduce noise and improves overall comfort.
Many energy-efficient glazing designs combine double glazing with low-e coatings to further control heat transfer and improve performance.
Single Glazing: When a Single Pane Still Makes Sense
Single glazing consists of a single pane of regular glass. While it offers minimal insulation, it is still used in certain situations, such as sheds, outbuildings, or heritage properties.
A single glazed window allows more heat transfer and is more likely to develop condensation, especially in colder climates. However, it can be a low-cost option where energy efficiency is not a primary concern.
Although modern buildings rarely rely on single glazing, it still has limited practical applications.
Glass Used in Window Glazing: What Types Perform Best?
The glass used in glazing systems varies depending on performance needs. Common types include tempered glass, laminated glass, and coated glass. Each type offers different benefits related to safety, strength, and insulation.
Advanced glazing systems may use low-e or low emissivity treatments, where a special coating is added to the glass to reflect heat while allowing visible light through. Some high-end systems even use xenon gas for superior insulation.
Choosing the right glass used in a glaze ensures durability, safety, and improved energy efficiency.
How Does Glaze Improve Energy Conservation and Energy Efficiency?
Glaze plays a critical role in energy conservation. By reducing solar heat gain in hot weather and minimizing heat loss in cold conditions, glazing helps stabilize indoor temperatures.
Features such as low-e coatings, gas-filled cavities, and insulated panes reduce the load on HVAC systems. This leads to lower energy costs and improved energy efficiency over time.
In areas with extreme temperatures, specialized glazing helps protect interiors while maintaining comfort throughout the year.
Choosing the Right Glazing Options for Your Climate
There are many glazing options available, and the right choice depends heavily on climates. Cold regions often benefit from triple glazing, while warmer regions may focus on solar control and UV reduction.
A professional glazier can help evaluate the pros and cons of different systems and recommend the most suitable type of glazing. The use of glazing should align with environmental conditions, building orientation, and budget.
Whether you plan to install new windows or upgrade existing ones, selecting the right glaze ensures long-term comfort, durability, and performance.
Professional Window Glazing & Installation in Clarksville, TN
Understanding the difference between glass and glazing is important—but having it installed correctly is what truly makes the difference. Allnite Glass provides professional window glazing and window installation services in Clarksville, TN, helping homeowners choose the right glass, glazing system, and configuration for long-term comfort and energy efficiency. Whether you are upgrading to double glazing, replacing outdated windows, or improving insulation and UV control, our experienced team ensures every window is properly sealed, fitted, and built to perform in Tennessee’s changing climate. Contact us today for a free quote!
Key Takeaways: What to Remember About Glaze and Window Glazing
- Glaze refers to the glass and the system that secures and enhances it
- Window glazing controls heat transfer, light, and comfort
- Double glazing significantly improves insulation and reduces heat loss
- Low-e and low emissivity coatings enhance energy efficiency
- Gas-filled cavities using argon or krypton improve insulation
- The frame and seals are just as important as the glass itself
- Climate plays a major role in choosing the right glazing solution
- Quality glazing and glass systems lower energy costs and improve indoor comfort