Glazing and Types of Window Glazing
In modern architecture and construction, window glazing plays a vital role in energy efficiency, safety, comfort, and aesthetics. Glazing refers to the process of installing glass into a window frame, but it also encompasses the many types of glass and techniques used to enhance building performance. From single-pane to triple-pane, from laminated to Low-E coated glass, each glazing type offers unique benefits.
Whether you're a homeowner seeking energy savings or a contractor choosing the right glass for your next build, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know about window glazing options and how to select the right one for your needs.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about glazing and different window glazing types, including Energy Saving options. Whether you're a homeowner or a professional in the field, this article is worth reading to gain a deep understanding of glazing options and make informed decisions for your projects.
Table of Contents
What is Glazing?
- Defining Glaze and Window Glazing
- The Importance of Glazing in Buildings
- Types of Glazing
- Single Glaze vs. Double Glaze
- Triple Glazing: Is it Worth It?
- Laminated Glass for Enhanced Safety
2. Understanding Glazing Types
- Annealed Glass and Its Applications
- Low-E Coatings for Energy Efficiency
- Tempered Glass: A Safety Game-Changer
- Float Glass and Its Versatility
3. Insulated Glazing
- How Does Insulation Work?
- Benefits of Insulated Glazing
- Factors to Consider When Choosing Insulation
4. Glazing in Practice
- Glazed Windows and Their Applications
- Clear Glass vs. Tinted Glass
- Stained Glass for Artistic Appeal
5. Installation Techniques
- Dry Glazing vs. Wet Glazing
- The Role of Putty in Glazing
- Triangular Glazing Points: What Are They?
6. Energy Efficiency
- Reducing Heat Transfer with Glazing
- Impact on Energy Costs
- Sustainable Choices for Greener Buildings
7. Safety Aspects
- The Importance of Safety Glass
- Laminated Safety Glass: How It Works
- Minimizing the Risk of Injury
8. Glazing Materials
- Glass Composition and Production
- Coatings Applied to Glass
- The Role of Polyvinyl Butyral (PVB)
9. Choosing the Right Glazing
- Factors Affecting Your Choice
- The Relationship Between Glazing and Energy Bills
- Sound Reduction and Window Glazing
Now, let's delve into each section to gain a more in-depth understanding of glazing and window glazing types.
1. What is Glazing?
Defining Glaze and Window Glazing
At its core, glazing refers to the installation of a pane of glass into a window sash or door. The term "glazing" can also be used more broadly to describe the practice of fitting glass into any structure. Glass is often used for its transparency, allowing natural light to enter a building while keeping the elements and outdoor noise at bay.
Glazing can be done using various types of glass, each offering unique properties and advantages. It's not just about selecting any piece of glass, but about making an informed choice based on your specific needs and preferences.
The Importance of Glazing in Buildings
The type of glazing you choose can have a significant impact on the performance of your building. It affects aspects such as energy efficiency, safety, and overall comfort. Proper glazing can reduce heat transfer, leading to lower energy costs and a more sustainable living or working space. It can also enhance safety by using materials like safety glass and laminated glass.
2. Types of Glazing

Single Glaze vs. Double Glaze
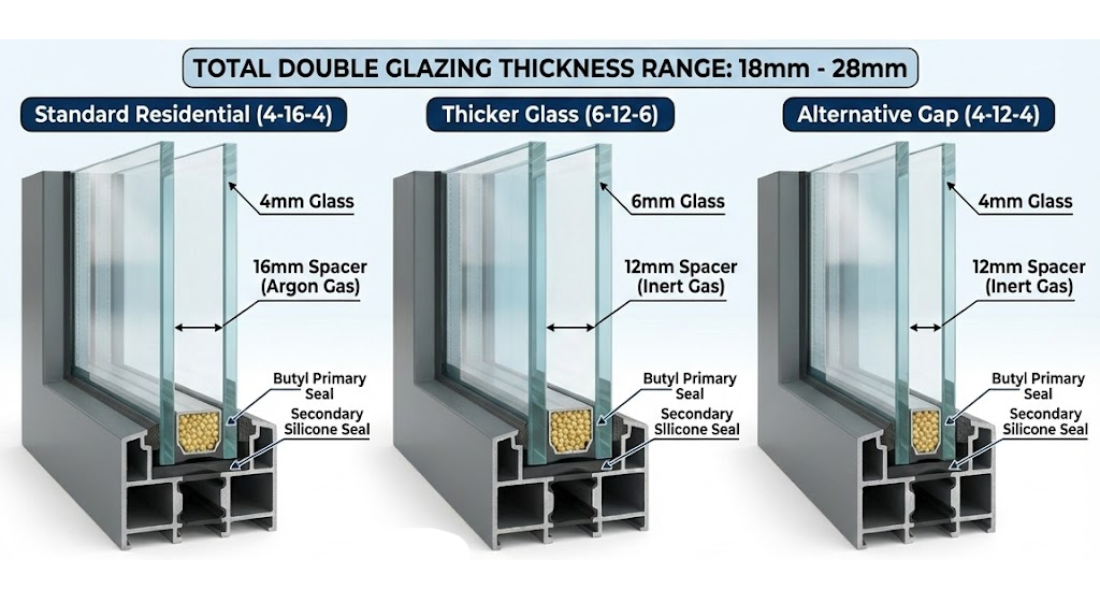
Single glazing involves a single pane of glass, while double glazing has a double pane with a gap between them. Single Pane Windows typically have lower insulation properties compared to double glazing, as they provide less resistance to heat transfer. Double glazed windows is known for its superior insulation properties, making it an excellent choice for enhancing energy efficiency. It helps maintain a comfortable indoor temperature by reducing heat transfer, ultimately leading to lower energy bills.
Single glazed windows, on the other hand, is still used in some applications, but it may not be the best choice for regions with extreme temperature variations.
Triple Glazing: Is it Worth It?
Triple glazing or also referred as triple pane window, is a three layers of glass. It provides even higher insulation levels than double glazing but comes at a higher cost. Before choosing triple glazing, consider your specific climate and energy efficiency goals.
Laminated Glass for Enhanced Safety
Laminated glass is produced by sandwiching a layer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) between two panes of glass. This design allows the glass to hold together even when it breaks, reducing the risk of injury. It's commonly used in applications where safety is a top priority, such as car windshields and high-rise buildings.
3. Understanding Glazing Types
Annealed Glass and Its Applications
Annealed glass is a common type of glass used in various applications. It is relatively simple to manufacture and can be cut and shaped easily. However, it is not as strong as tempered glass and does not offer the same safety benefits.
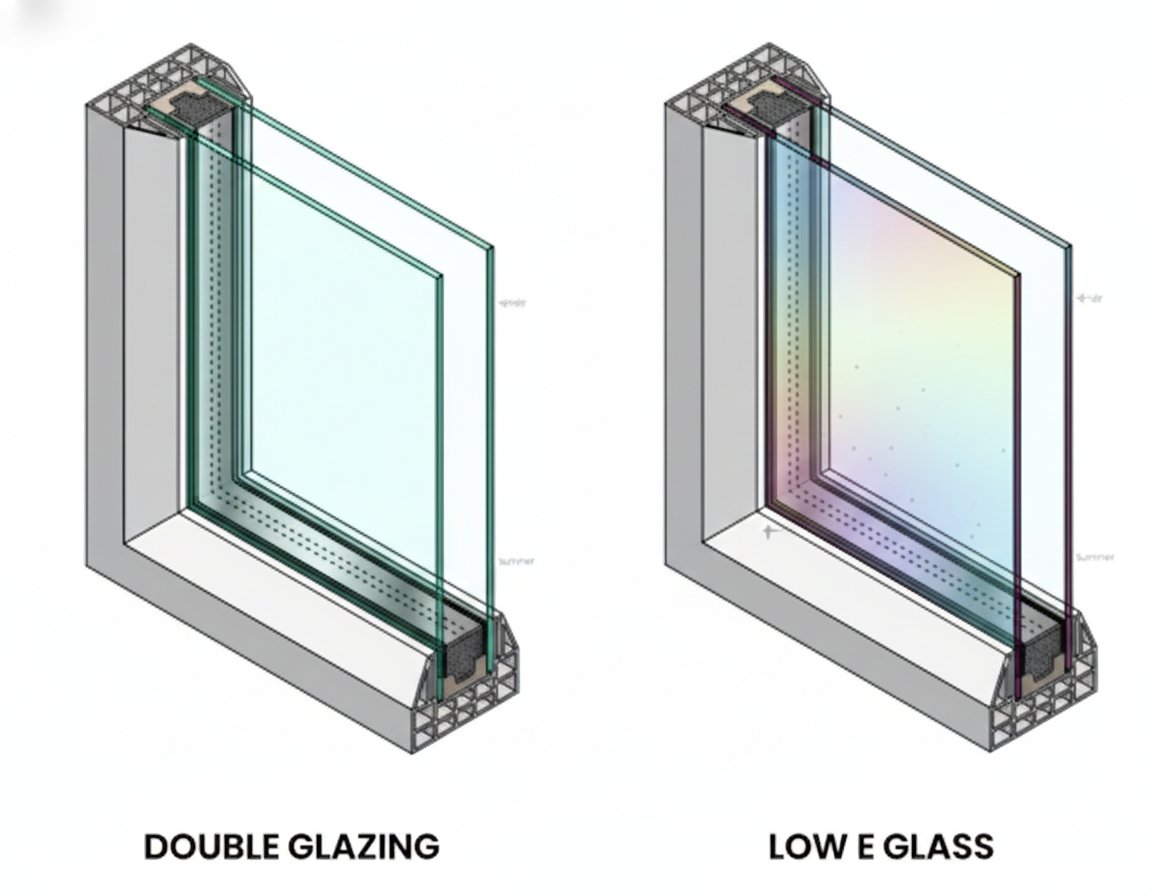
Low-E Coatings for Energy Efficiency
Low emissivity (Low-E) coatings are thin, virtually invisible layers applied to glass surfaces. They help reduce heat transfer, making your building more energy efficient. Low-E glass is an excellent choice for regions with extreme temperatures as it keeps the indoor environment comfortable year-round.
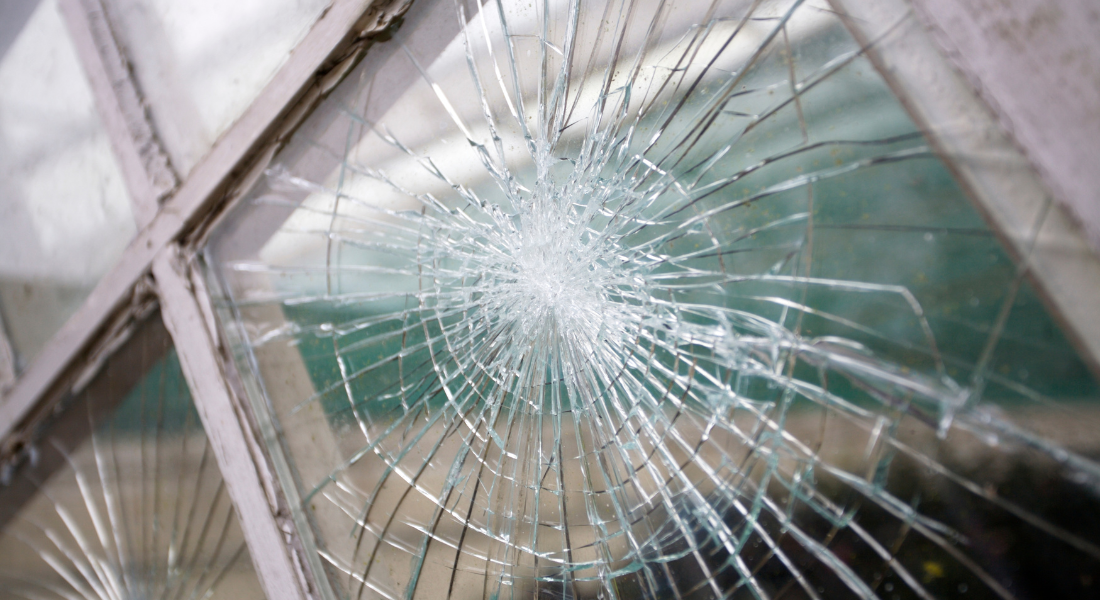
Tempered Glass: A Safety Game-Changer
Tempered glass is manufactured through a special heating and cooling process, making it significantly stronger than regular glass. When it breaks, it shatters into small, dull-edged pieces, reducing the risk of injury. This type of glazing is commonly used in applications where safety is a top priority, such as shower doors and glass railings.
Float Glass and Its Versatility
Float glass is one of the most common types of glass used in construction. It is produced by melting raw materials into molten glass, which is then floated on a bed of molten tin. This process creates a smooth, distortion-free surface, making it an ideal choice for windows and facades.
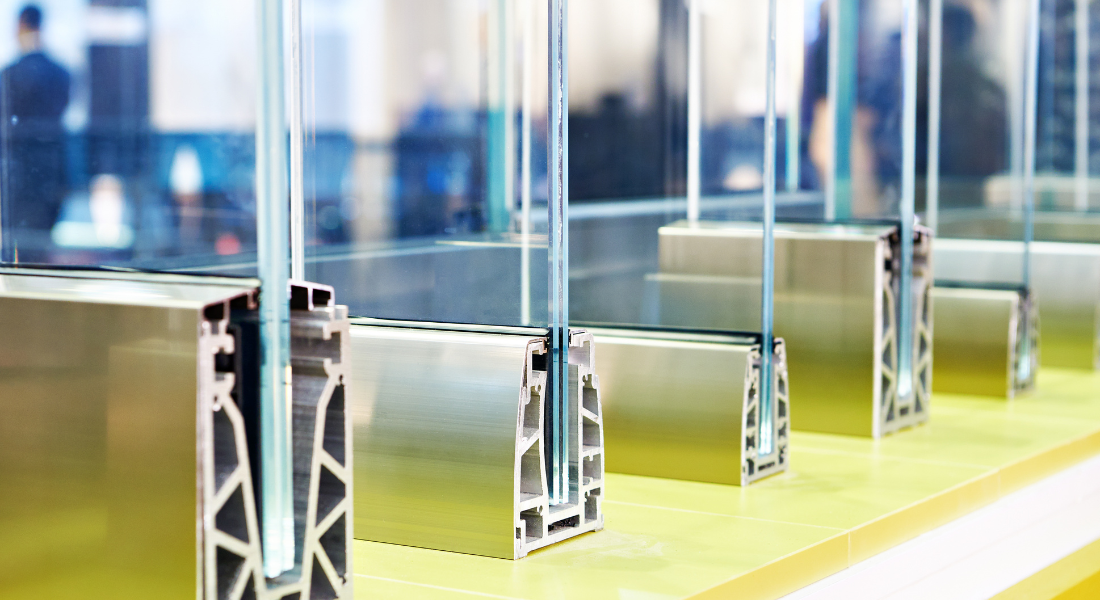
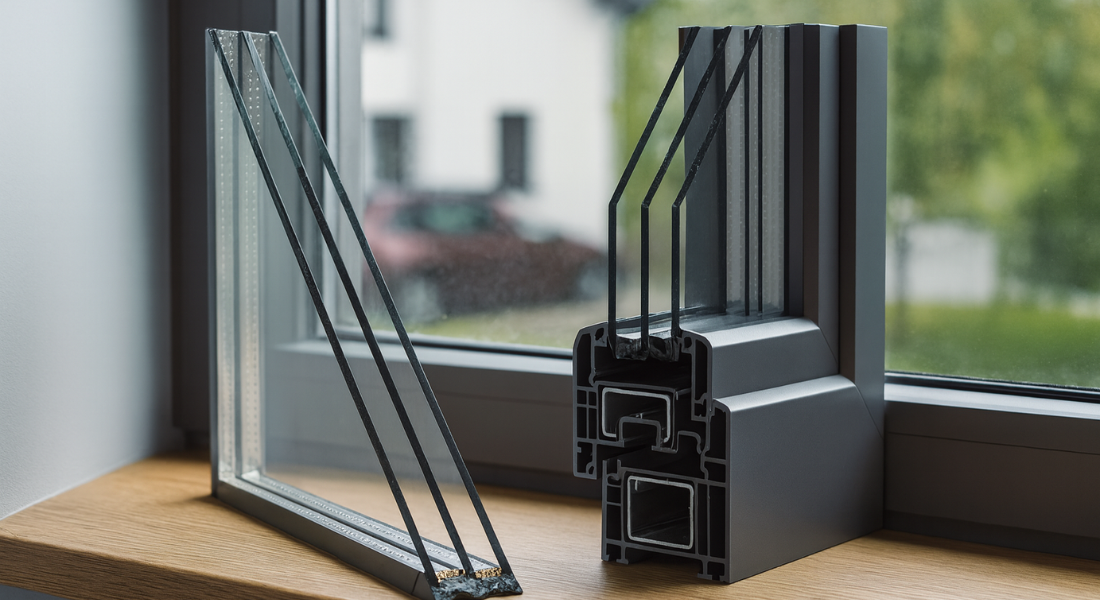
4. Insulated Glazing
How Does Insulation Work?
Insulated glazing involves using multiple layers of glass with a gap between them. This gap is typically filled with air or gas, creating a barrier that reduces heat transfer. The more layers you have, the better the insulation.
Benefits of Insulated Glazing
Insulated glazing offers several benefits, including enhanced energy efficiency, reduced condensation, and improved sound insulation. It is an excellent choice for those looking to create a comfortable and quiet indoor environment.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Insulation
When selecting insulated glazing, consider the type of gas used to fill the gap, the number of layers, and the thickness of the glass. These factors can impact the level of insulation provided and the overall performance of your windows.
5. Glazing in Practice
Glazed Windows and Their Applications
Glazed windows are a common choice for both residential and commercial buildings. They allow natural light to enter while keeping the elements outside. You can choose from various glazing types to achieve specific goals, such as energy efficiency, safety, or aesthetics.
Clear Glass vs. Tinted Glass
Clear glass is the most common choice for windows, offering unobstructed views and ample natural light. Tinted glass, on the other hand, can help reduce glare and heat gain, making it a suitable option for buildings in sunny climates.
Stained Glass for Artistic Appeal
Stained glass is an artistic and decorative form of glazing. It adds a unique and aesthetic element to windows, often found in churches and historic buildings. Stained glass allows the play of colors and patterns, creating a visually stunning effect.
6. Installation Techniques
Dry Glazing vs. Wet Glazing
The installation of glass can be done using dry glazing or wet glazing techniques. Dry glazing involves using gaskets and pressure plates to secure the glass, while wet glazing uses sealants. The choice between these methods can affect the aesthetics, insulation, and maintenance of your windows.
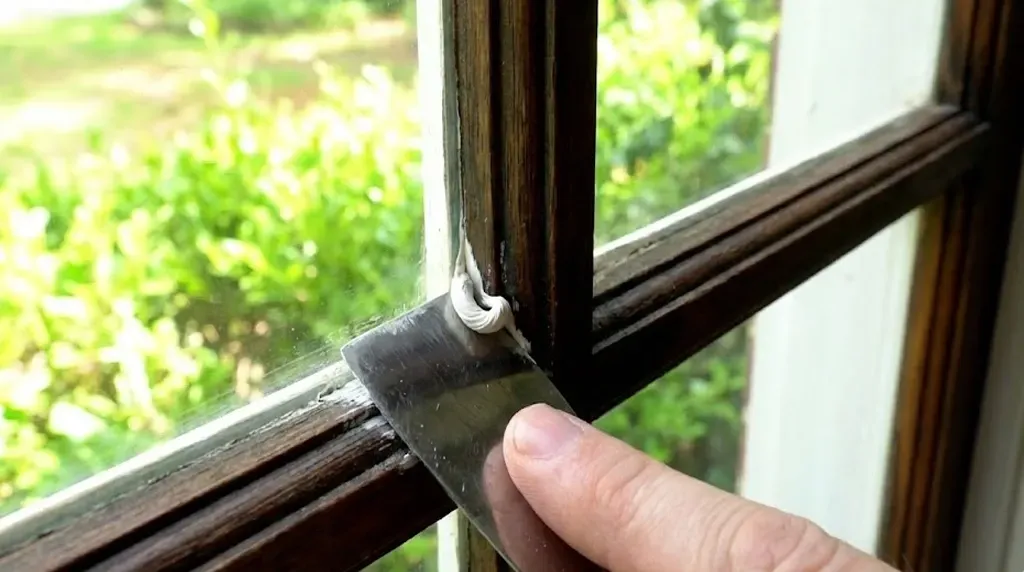
The Role of Putty in Glazing
Glazing putty is used to seal glass panes in windows, creating a secure barrier that protects against drafts and moisture. To apply it, a putty knife is typically used to spread the putty evenly around the edges of the glass, ensuring a smooth and tight seal. This method has been around for many years and is often used for restoring older windows. However, putty can crack or dry out over time, leading to leaks and requiring maintenance. While putty is affordable and easy to work with, modern alternatives like silicone sealants offer more durability and energy efficiency.
Triangular Glazing Points: What Are They?
Triangular glazing points are small, triangular pieces of metal or plastic used to hold the glass in place during installation. They are a simple yet effective way to secure the glass within the window frame. Understanding their use can be valuable for DIY projects or when working with professionals.
7. Energy Efficiency
Reducing Heat Transfer with Glazing
One of the key benefits of choosing the right glazing is the ability to reduce heat transfer. Properly insulated windows can keep your indoor environment more comfortable by preventing heat from escaping during cold weather and entering during hot weather.
Impact on Energy Costs
By reducing heat transfer, the right glazing can significantly impact your energy bills. Choosing the right type of glazing for your climate and energy efficiency goals can lead to substantial savings over time.
Sustainable Choices for Greener Buildings
As the importance of sustainability grows, selecting energy-efficient glazing is a crucial step in creating greener buildings. Sustainable glazing options not only reduce energy consumption but also contribute to a more environmentally friendly construction industry.
8. Safety Aspects
The Importance of Safety Glass
Safety glass is designed to minimize the risk of injury when it breaks. It's a crucial choice for applications where accidents can occur, such as glass doors or partitions. Understanding the importance of safety glass is essential for creating safe and secure environments.
Laminated Safety Glass: How It Works
Laminated safety glass holds together when it breaks, thanks to the polyvinyl butyral (PVB) layer. This design makes it an excellent choice for automotive windshields, glass floors, and other applications where safety is a top priority.
Minimizing the Risk of Injury
Choosing the right glazing, especially for areas with high potential for accidents, can greatly reduce the risk of injury. Understanding the properties and benefits of safety glass can help you make safer choices for your projects.
9. Glazing Materials
Glass Composition and Production
Glass is made by melting raw materials into molten glass, which is then shaped into sheets or panes. Understanding the composition and production process of making a sheet of glass can help you appreciate its versatility and strength.
Coatings Applied to Glass
Various coatings can be applied to glass to enhance its properties, such as low emissivity (Low-E) coatings for energy efficiency. Learning about these coatings and their benefits can help you make informed choices when selecting glazing.
The Role of Polyvinyl Butyral (PVB)
Polyvinyl butyral (PVB) is a crucial component in laminated glass. It's the layer that holds the glass together when it breaks, reducing the risk of injury. Understanding the role of PVB in glazing materials can help you appreciate the safety benefits it provides.
10. Choosing the Right Glazing
Factors Affecting Your Choice
When selecting window glazing compound for your project, consider factors such as your climate, energy efficiency goals, and safety requirements.
The Relationship Between Glazing and Energy Bills
By choosing energy-efficient glazing, you can effectively lower your energy bills. This relationship between glazing and energy costs should be a key consideration when planning your construction or renovation projects.
Sound Reduction and Window Glazing
In addition to insulation, the right glazing can also provide sound reduction benefits. This is particularly important for buildings located in noisy areas. Understanding how different glazing types affect sound insulation can help you create a quieter indoor environment.
Conclusion
In the world of construction and architecture, the choice of glazing can have a profound impact on a building's performance, safety, and energy efficiency. By understanding the various glazing types and their properties, you can make informed decisions that enhance the comfort and functionality of your space while contributing to a more sustainable and safer environment.
In summary, here are the most important things to remember about glazing and window glazing types:
- Glazing involves the installation of a pane of glass into a window sash or door.
- The type of glazing you choose can significantly impact energy efficiency, safety, and overall comfort.
- Single-glazing, double-glazing, and triple glazing offer different levels of insulation and energy efficiency.
- Laminated glass provides enhanced safety by holding it together when it breaks.
- Various types of glass, including annealed, low-E, tempered, and float glass, have unique applications and properties.
- Insulated glazing reduces heat transfer, enhances energy efficiency, and minimizes condensation.
- The choice of installation technique, such as dry glazing or wet glazing, can affect aesthetics and insulation.
- When thinking about window replacement, energy-efficient glazing options can help reduce your energy bills and support sustainability.
- Safety glass, including laminated safety glass, reduces the risk of injury.
- Understanding the composition and coatings of glass can help you make informed choices.
- Consider your climate, energy efficiency goals, and safety requirements when choosing the right glazing for your project.
What is glazing and types of glazing?
The term window glazing refers to the process of installing glass in windows, doors, or walls. It also pertains to the glass itself, which can vary in terms of its properties and uses. The types of glazing include:
- Single Glazing: A single pane of glass, often used in older homes. It provides minimal insulation.
- Double Glazing: Consists of two panes of glass with a gap in between, usually filled with air or inert gas like argon, offering better thermal insulation.
- Triple Glazing: Three panes of glass with two gaps, providing superior insulation and energy efficiency.
- Low-E (Low Emissivity) Glazing: Coated glass that reflects infrared and ultraviolet rays while allowing visible light to pass through, enhancing energy efficiency.
- Laminated Glazing: Two or more layers of glass bonded with a plastic interlayer, providing increased security and noise reduction.
- Tempered Glazing: Heat-treated glass that is stronger and breaks into small, less dangerous pieces upon impact.
- Tinted Glazing: Glass with a color added to reduce glare and heat from sunlight.
- Decorative Glazing: Includes stained glass, frosted glass, or patterned glass used for aesthetic purposes.
What is the glazing of a window?
The glazing of a window refers to the glass installed within the window frame. This glass can vary in type, thickness, and treatment to provide different levels of insulation, security, and aesthetic appeal. The glazing is an essential component that affects the window's thermal performance, sound insulation, and overall functionality.
What is the most common type of glazing?
The most common type of glazing in modern buildings is double glazing. It strikes a balance between cost, energy efficiency, and comfort. Double glazing significantly reduces heat loss compared to single glazing, making it the preferred choice for residential and commercial properties seeking to improve energy efficiency and reduce heating and cooling costs.
What are the different types of glazing bars?
Glazing bars, also known as muntins or sash bars, are the elements that divide a window into smaller panes. The different types include:
- Traditional Glazing Bars: These are integral to the window frame, creating individual panes of glass separated by the bars.
- Applied Glazing Bars: Bars applied to the surface of a single pane of glass, giving the appearance of divided panes without actual separations.
- Spacer Glazing Bars: Found within double or triple glazed units, these bars are located between the panes of glass, separating and supporting them.
- Simulated Divided Lites (SDL): Combine applied bars on both the interior and exterior of the glass with a spacer bar in between, mimicking the look of true divided lites.
- Georgian Bars: Specifically styled bars often used in period or traditional properties to replicate historic window designs.
Each type of glazing bar serves different aesthetic and functional purposes, contributing to the overall look and performance of the window.
With this knowledge, you can make confident decisions when selecting the glazing type that best suits your needs and goals. Whether you're focused on energy efficiency, safety, or aesthetics, there is a glazing solution that meets your requirements.